Cost, volume, profit analysis-Problem 1
Q. A company has the following budget on orders from home market

At this level of output the company has spare capacity and it is therefore planning to develop export market. It believes that it will be able to sell an additional 750 units – the limit of its production due to shortage of raw materials. No additional fixed costs would be incurred and selling price and variable costs per unit would be same as for the home market.
Before launching its export campaign, however , the company is approached by a home buyer who wishes to purchase 200 deluxe models which twice as much materials as the standard model. What is the minimum price which should be charged if this order is accepted?
Ans. From the data given above for 2000 units we can find the contribution per unit:-
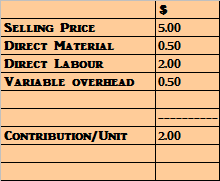
The company has spare capacity to manufacture 750 additional units which it can sell in the export. -------------------(Given)
The contribution which the company can obtain from the sale of these 750 units
= 750 * 2 = $1,500
The company’s capacity is limited by the availability of raw materials.
So the total cost of raw materials available = 2750 * .5 = $1,375
The new deluxe product which the home buyer needs requires twice the raw material.
So if the company manufactures 200 units of the deluxe product it will have spare capacity to manufacture only 350 additional units of the standard product.
Contribution from the 350 units of standard product = 350 * 2 = $700
The company can only take the order if the contribution from the 200 units of deluxe product and 350 units of standard product equals to the 750 units of the normal product.
Contribution needed from the 200 units of deluxe product = 1500 - 350 * 2 = $800.
Contribution/unit of deluxe product = $4
The cost of the deluxe product is

So in order to take the order for 200 units of deluxe product the company must charge a minimum price of 3.5 + 4= $7.5
Q. A company has the following budget on orders from home market
At this level of output the company has spare capacity and it is therefore planning to develop export market. It believes that it will be able to sell an additional 750 units – the limit of its production due to shortage of raw materials. No additional fixed costs would be incurred and selling price and variable costs per unit would be same as for the home market.
Before launching its export campaign, however , the company is approached by a home buyer who wishes to purchase 200 deluxe models which twice as much materials as the standard model. What is the minimum price which should be charged if this order is accepted?
Ans. From the data given above for 2000 units we can find the contribution per unit:-
The company has spare capacity to manufacture 750 additional units which it can sell in the export. -------------------(Given)
The contribution which the company can obtain from the sale of these 750 units
= 750 * 2 = $1,500
The company’s capacity is limited by the availability of raw materials.
So the total cost of raw materials available = 2750 * .5 = $1,375
The new deluxe product which the home buyer needs requires twice the raw material.
So if the company manufactures 200 units of the deluxe product it will have spare capacity to manufacture only 350 additional units of the standard product.
Contribution from the 350 units of standard product = 350 * 2 = $700
The company can only take the order if the contribution from the 200 units of deluxe product and 350 units of standard product equals to the 750 units of the normal product.
Contribution needed from the 200 units of deluxe product = 1500 - 350 * 2 = $800.
Contribution/unit of deluxe product = $4
The cost of the deluxe product is
So in order to take the order for 200 units of deluxe product the company must charge a minimum price of 3.5 + 4= $7.5